Filtering and Sorting
Filtering and Sorting help users quickly find and organize scraped data in the Results page.
For example, if your scraper returns product data, users can:
- Filter to show only available items under $50
- Sort by price (low to high) or reviews (high to low)
These controls appear above the data table in the Results page.
Creating a Simple Filter
To add filters, pass a filters array when adding your scraper.
import { Server } from "botasaurus-server/server"
import { filters } from "botasaurus-server/ui"
import { scrapeProductData } from "../src/scrapeProductData"
Server.addScraper(scrapeProductData, {
filters: [new filters.SearchTextInput("product_name")]
})
How it works
filters.SearchTextInput('product_name')adds a search box forproduct_namefieldServer.addScraper(..., { filters: [...] })adds the filter to your scraper
With this, users can now filter products by typing in the search box.

Types of Filters
There are 12 types of filters. All filters accept an optional label parameter to customize the display text. If label is not provided, the field name appears in Title Case.
MinNumberInput
A number input that shows items where the target field is ≥ the entered number
Example
new filters.MinNumberInput("price")
MaxNumberInput
A number input that shows items where the target field is ≤ the entered number
Example
new filters.MaxNumberInput("price")
IsTrueCheckbox
A checkbox that shows items where the target field is strictly true.
Example
new filters.IsTrueCheckbox("is_available")
IsFalseCheckbox
A checkbox that shows items where the target field is strictly false.
Example
new filters.IsFalseCheckbox("is_available")
IsTruthyCheckbox
A checkbox that shows items where the target field is truthy (e.g., true, 1, "hello").
Example
new filters.IsTruthyCheckbox("description")
IsFalsyCheckbox
A checkbox that shows items where the target field is falsy (e.g., false, 0, "", null).
Example
new filters.IsFalsyCheckbox("description")
IsNullCheckbox
A checkbox that shows items where the target field is strictly null.
Example
new filters.IsNullCheckbox("description")
IsNotNullCheckbox
A checkbox that shows items where the target field is not strictly null.
Example
new filters.IsNotNullCheckbox("description")
SingleSelectDropdown
A dropdown for picking a single option. It requires an options array.
The filter matches if:
- The target field is a
Stringand exactly matches the selected option. - The target field is an
Arrayand includes the selected option.
Additional Options
caseInsensitive: Perform case-insensitive matching. Whentrue, "Electronics" will match "electronics", "ELECTRONICS", etc. Defaults tofalse.
Example
new filters.SingleSelectDropdown("category", {
options: [
{ value: "apparel", label: "Apparel" },
{ value: "electronics", label: "Electronics" }
]
})
MultiSelectDropdown
A dropdown for picking multiple options. It requires an options array.
The filter matches if:
- The target field is a
Stringand matches any of the selected options. - The target field is an
Arrayand includes any of the selected options.
Additional Options
caseInsensitive: Perform case-insensitive matching. Whentrue, "Cotton" will match "cotton", "COTTON", etc. Defaults tofalse.
Example
new filters.MultiSelectDropdown("tags", {
options: [
{ value: "cotton", label: "Cotton" },
{ value: "casual", label: "Casual" },
{ value: "computer", label: "Computer" },
{ value: "portable", label: "Portable" }
]
})
BoolSelectDropdown
A dropdown with "Yes" and "No" options for filtering truthy/falsy values.
- "Yes" keeps rows where the target field is truthy (e.g.,
true,1,"hello"). - "No" keeps rows where the target field is falsy (e.g.,
false,0,"",null).
It is an alternative to checkbox, often clearer to users than a checkbox.
Additional Options
prioritizeNo: Iftrue, "No" will be the first option in the dropdown instead of "Yes". Defaults tofalse.invertFilter: Iftrue, "Yes" filters for falsy values and "No" filters for truthy ones. Defaults tofalse.
Example
new filters.BoolSelectDropdown("is_available")
SearchTextInput
A text input that shows items where the target field's value contains the search term (case-insensitive).
Example
new filters.SearchTextInput("name")
Creating a Simple Sort
Sorts are added exactly the same way as filters.
import { Server } from "botasaurus-server/server"
import { sorts } from "botasaurus-server/ui"
import { scrapeProductData } from "../src/scrapeProductData"
Server.addScraper(scrapeProductData, {
sorts: [
// A simple sort by price
new sorts.NumericAscendingSort("price"),
// A custom, multi-level sort preset
new sorts.Sort({
label: "Top Rated",
isDefault: true,
sorts: [
new sorts.NumericDescendingSort("reviews"),
new sorts.TrueFirstSort("is_available"),
]
})
]
})
How it works:
sorts.NumericAscendingSort('price')creates a sort option for thepricefield.sorts.Sort()combines multiple sorting criteria into a single sort option, it first sorts by reviews, then by products whereis_availableis True.- In
sorts.Sort,isDefaultis set totrue. With this, the "Top Rated" sort will be automatically applied to data when the Results page first loads. Server.addScraper(..., { sorts: [...] })adds the sorts to your scraper
With this, users can now sort products

Types of Sorts
There are 13 types of sorts.
Each sort accepts two optional properties:
label: text shown in the dropdown. If not provided, it is automatically generated based on field name.isDefault: apply this sort automatically when the Results page loads. Defaults tofalse.
We recommend setting one of the sorts as default (isDefault: true) to ensure data is meaningfully organized when users first view the Results page.
AlphabeticAscendingSort
Sorts items by the target field in ascending alphabetical order (A-Z).
Example
new sorts.AlphabeticAscendingSort("name")
AlphabeticDescendingSort
Sorts items by the target field in descending alphabetical order (Z-A).
Example
new sorts.AlphabeticDescendingSort("name")
NumericAscendingSort
Sorts items by the target field in ascending numerical order.
Example
new sorts.NumericAscendingSort("price")
NumericDescendingSort
Sorts items by the target field in descending numerical order.
Example
new sorts.NumericDescendingSort("price")
NewestDateFirstSort
Sorts items by a date field in newest date first order.
Example
new sorts.NewestDateFirstSort("created_at")
OldestDateFirstSort
Sorts items by a date field in oldest date first order.
Example
new sorts.OldestDateFirstSort("created_at")
TrueFirstSort
Sorts items where the target field is true first.
Example
new sorts.TrueFirstSort("is_available")
FalseFirstSort
Sorts items where the target field is false first.
Example
new sorts.FalseFirstSort("discounted")
TruthyFirstSort
Sorts items where the target field has a truthy value first.
Example
new sorts.TruthyFirstSort("description")
FalsyFirstSort
Sorts items where the target field has a falsy value first.
Example
new sorts.FalsyFirstSort("description")
NullsFirstSort
Sorts items where the target field is null first.
Example
new sorts.NullsFirstSort("end_date")
NullsLastSort
Sorts items where the target field is null last.
Example
new sorts.NullsLastSort("end_date")
Sort
Combines multiple sorting criteria into a single sort option. Sorts are applied in the order they are listed.
Example
new sorts.Sort({
label: "Top Products",
sorts: [
new sorts.AlphabeticAscendingSort("name"),
new sorts.NumericDescendingSort("reviews"),
new sorts.TrueFirstSort("is_available")
]
})
Real World Example
Let's say your scraper returns the following product data:
const taskScraper = task({
name: "taskScraper",
run: () => {
return [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "T-Shirt",
"price": 16, // in US Dollar
"reviews": 1000,
"is_available": true,
"category": "apparel",
"tags": ["cotton", "casual"]
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Laptop",
"price": 700,
"reviews": 500,
"is_available": false,
"category": "electronics",
"tags": ["computer", "portable"]
}
];
},
})
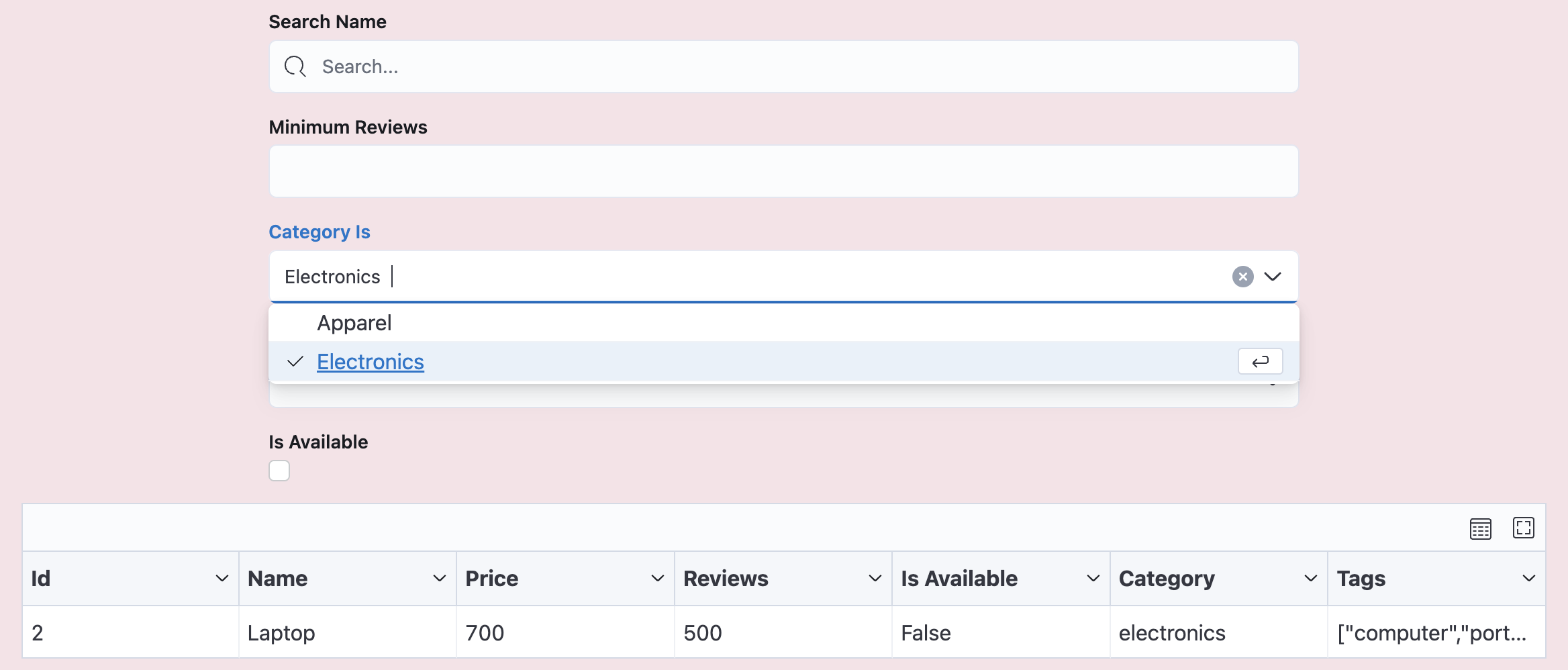
Now you want to add filters to help users find specific products. The following code adds filters that allow users to:
- Search for products by name
- Filter by minimum number of reviews
- Filter by product category
- Filter by product tags
- Show only available products
import { Server } from "botasaurus-server/server"
import { filters } from "botasaurus-server/ui"
import { scrapeProductData } from "../src/scrapeProductData"
const allFilters = [
new filters.SearchTextInput("name"),
new filters.MinNumberInput("reviews", { label: "Minimum Reviews" }),
new filters.SingleSelectDropdown("category", {
options: [
{ value: "apparel", label: "Apparel" },
{ value: "electronics", label: "Electronics" }
]
}),
new filters.MultiSelectDropdown("tags", {
options: [
{ value: "cotton", label: "Cotton" },
{ value: "casual", label: "Casual" },
{ value: "computer", label: "Computer" },
{ value: "portable", label: "Portable" }
]
}),
new filters.IsTrueCheckbox("is_available", { label: "Is Available" })
]
Server.addScraper(
scrapeProductData,
{ filters: allFilters }
)
With these filters in place, users can easily get the data they want:
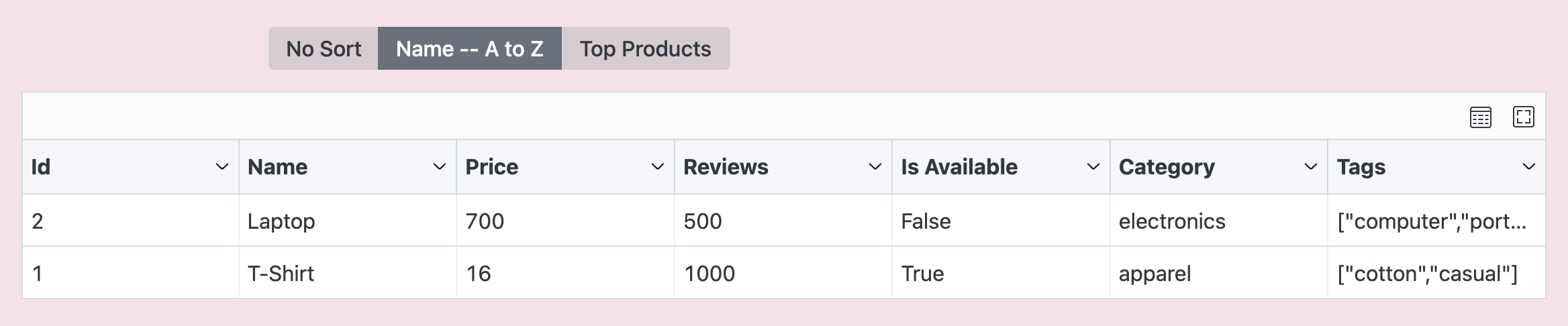
Next, you want to add sorts to order products. The following code allows users to:
- Sort products by name in ascending order
- Use a combined sort that orders products by:
- Name alphabetically
- Number of reviews (highest first)
- Availability (available products first)
import { Server } from "botasaurus-server/server"
import { sorts } from "botasaurus-server/ui"
import { scrapeProductData } from "../src/scrapeProductData"
const allSorts = [
new sorts.AlphabeticAscendingSort("name"),
new sorts.Sort({
label: "Top Products",
isDefault: true,
sorts: [
new sorts.AlphabeticAscendingSort("name"),
new sorts.NumericDescendingSort("reviews"),
new sorts.TrueFirstSort("is_available")
]
})
]
Server.addScraper(
scrapeProductData,
{ sorts: allSorts }
)
Now users can sort the product data: