Adding an API
Botasaurus allows you to expose your scrapers as APIs, enabling you to:
- Consume scrapers from web apps, cron jobs, or other workflows
- Run your scrapers on cloud VMs for scalable, always-on automation
- Monetize your scrapers by listing them on marketplaces like RapidAPI
How to Add an API to Your App
To enable API call ApiConfig.enableApi() in src/scraper/backend/api-config.ts file:
import ApiConfig from "botasaurus-server/api-config";
// Enable the API
ApiConfig.enableApi();
What happens after enabling the API:
-
Your app displays an
API Integrationtab containing auto-generated documentation and code examples specific to your scrapers.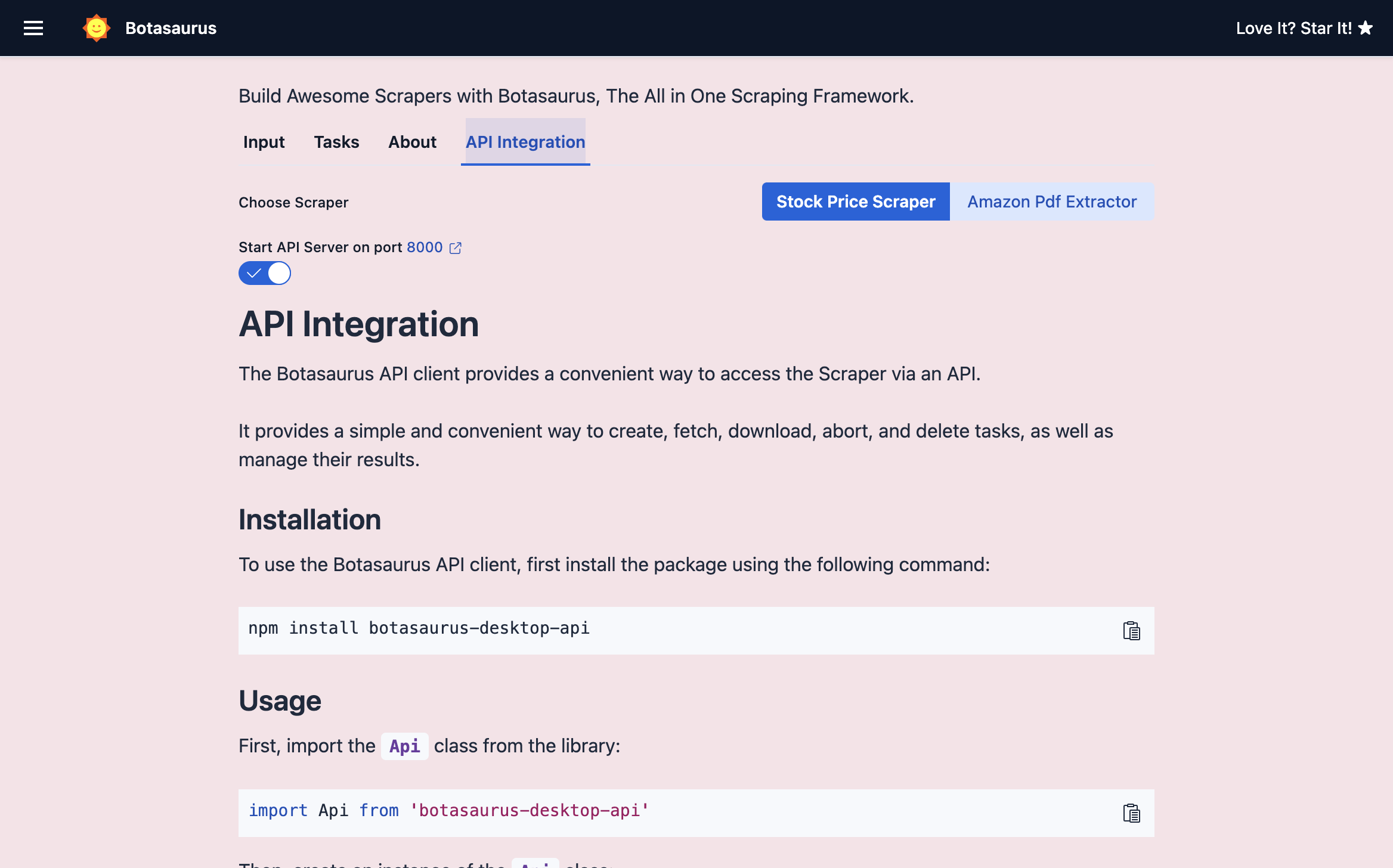
-
When your app launches, an API server starts at
http://localhost:8000(default). This URL also also displays your API documentation.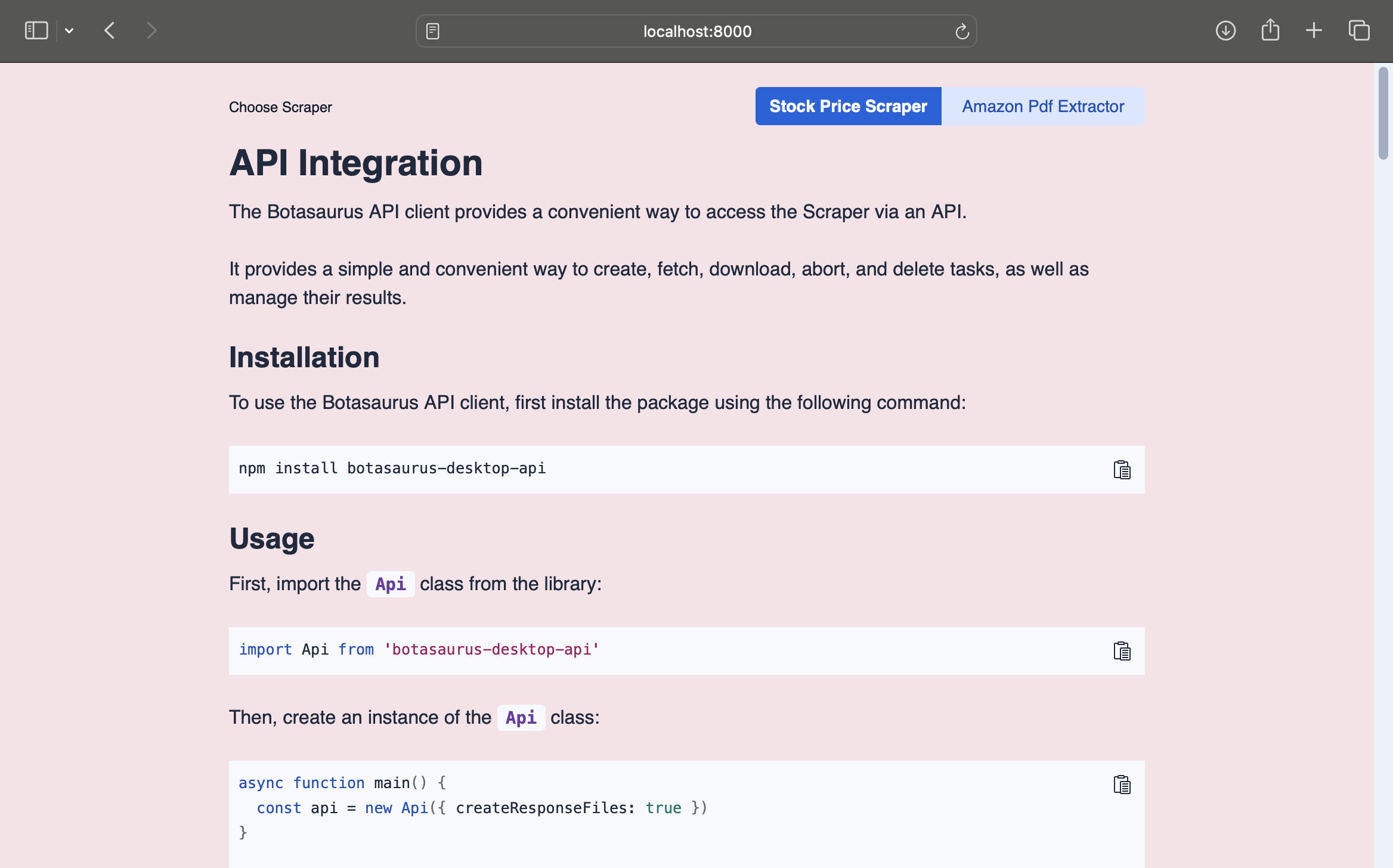
- The API is built on Fastify for low latency and production-ready performance
- It automatically enforces any rate limits you've defined for your scrapers
- It validates incoming requests against the controls defined in your scraper's
inputsfolder, rejecting invalid requests with a400error to protect your scrapers from bad data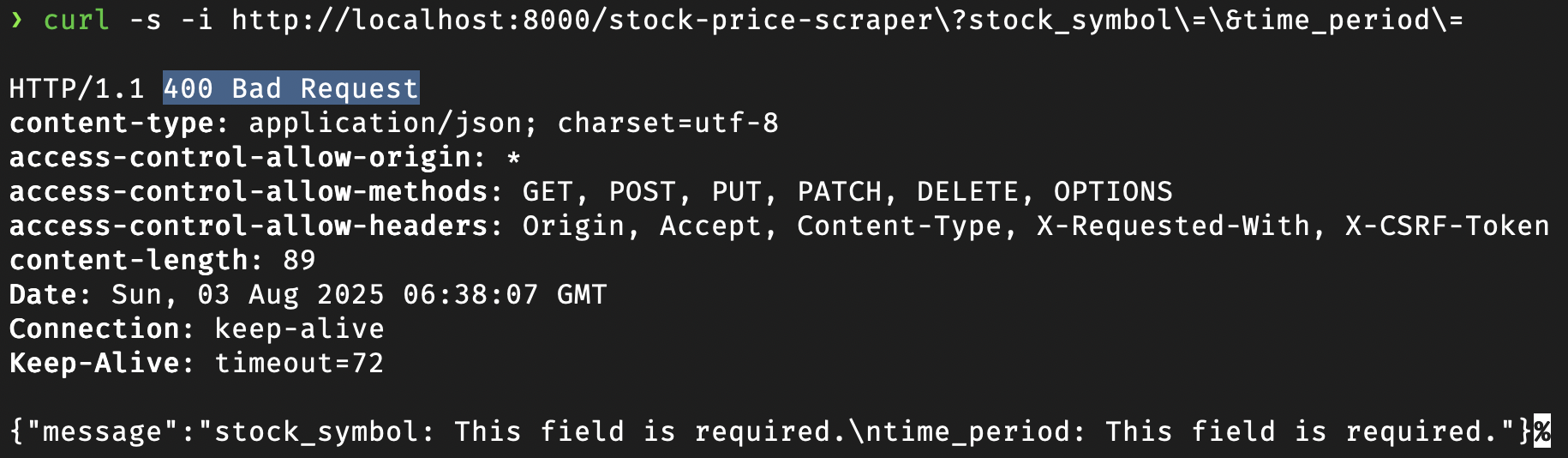
We recommend reading the generated API documentation to understand and effectively configure your API.
Configuration Options
The ApiConfig class provides 5 methods to configure your API's behavior:
setApiPort(port: number)
Changes the port where the API server listens. The default is port 8000.
Example:
// Set API to run on port 8080
ApiConfig.setApiPort(8080);
When to use: When port 8000 is already in use or you want to run on a specific port.
disableApiAutostart()
Prevents the API server from starting automatically when the app launches. Users must manually start the API from the "API" tab.
Example:
// API will not run until manually started from the desktop GUI
ApiConfig.disableApiAutostart();
Note: Botasaurus remembers toggle settings. If a user turns the API on, it will start automatically on the next app launch.
When to use: When you want users to explicitly enable the API before using it. Note that disabling API autostart doesn't reduce startup time, as the API server is lightweight and launches after the desktop app finishes loading.
setApiBasePath(path: string)
Adds a prefix to all API routes, useful for mounting the API under a specific subpath like /v1 or /api.
Example:
// Prefixes all routes with /v1
ApiConfig.setApiBasePath("/v1");
When to use:
- Hosting multiple APIs on one server
- Implementing API versioning (
/v1,/v2)
addScraperAlias(scraper: Scraper, endpoint: string)
Creates a direct GET endpoint for running scrapers without the overhead of creating, scheduling, and running tasks.
Example:
import { hotelsSearchScraper } from "../src/scrapers";
// Creates direct GET endpoint at /hotels/search
ApiConfig.addScraperAlias(hotelsSearchScraper, "/hotels/search");
This allows you to:
- Make direct GET requests to the
/hotels/searchendpoint - Execute the scraper immediately, bypassing task creation, scheduling, and running overhead
- Validate input data before execution, returning a
400error for invalid requests - Cache results based on the provided parameters
- Respect the rate limits defined for your scraper
When to use:
- Simple scraper calls without task management overhead
- Custom endpoint naming
- Reselling APIs via platforms like RapidAPI, where task abstraction is unnecessary
addCustomRoutes((server: FastifyInstance) => void)
Extends the API with custom endpoints and middleware using Fastify's routing system. This method receives a Fastify instance, allowing you to define any route you need.
Example: Adding a custom health check endpoint
ApiConfig.addCustomRoutes((server) => {
server.get('/health', (request, reply) => {
return reply.send({ status: 'OK'});
});
});
Example: Adding validation middleware
ApiConfig.addCustomRoutes((server) => {
server.addHook('onRequest', (request, reply, done) => {
// Check for secret
const secret = request.headers['x-secret'] as string;
if (secret === '49cb1de3-419b-4647-bf06-22c9e1110313') {
// Valid secret, proceed
return done();
} else {
return reply.status(401).send({
message: 'Unauthorized: Invalid secret.',
});
}
});
});
When to use:
- Adding authentication middleware
- Creating custom endpoints
- Implementing webhook receivers
Complex Example
Here's a comprehensive configuration that demonstrates multiple options working together:
import ApiConfig from 'botasaurus-server/api-config';
import { hotelsSearchScraper } from "../src/scrapers";
// Enable API functionality
ApiConfig.enableApi();
// Production configuration
ApiConfig.setApiPort(3000);
ApiConfig.setApiBasePath("/v1");
// Add scraper aliases for direct access
ApiConfig.addScraperAlias(hotelsSearchScraper, '/hotels/search');
// Add custom routes
ApiConfig.addCustomRoutes((server) => {
// Health check for monitoring
server.get('/health', (request, reply) => {
return reply.send({ status: 'OK'});
});
// Authentication middleware
server.addHook('onRequest', (request, reply, done) => {
// Check for secret
const secret = request.headers['x-secret'] as string;
if (secret === '49cb1de3-419b-4647-bf06-22c9e1110313') {
// Valid secret, proceed
return done();
} else {
return reply.status(401).send({
message: 'Unauthorized: Invalid secret.',
});
}
});
});
With this configuration:
- The API runs on port 3000
- All routes are prefixed with
/v1 - Hotel search is available at GET
/v1/hotels/search - Health check is available at GET
/v1/health - All requests require authentication via the
x-secretheader